Hierarchical/tree database for directories path in filesystem(文件系统中目录路径的分层/树数据库)
问题描述
我想将目录(存在于磁盘上)存储到数据库中,维护它们的层次结构/树结构.
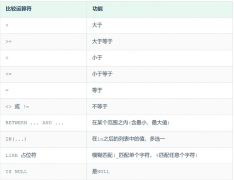
这是一个数字:
<前>(根)/目录 2 目录 3/ 目录 4 目录 5 目录 6/目录7我正在使用 SQLite 数据库.
请推荐我:
将上述结构存储在 SQLite 数据库中的 SQL 查询,以及
当我选择一个时检索目录完整路径的查询.
即假设我选择
Dir7那么我应该得到像ROOT/Dir2/Dir4/Dir7 这样的完整路径
这是 SQLite 的快速闭包表示例.我没有包括将项目插入现有树的语句.相反,我只是手动创建了语句.您可以在分层数据模型幻灯片中找到插入和删除语句.
在为目录插入 ID 时,为了我的理智,我重命名了目录以匹配它们的 ID:
(ROOT)/目录 2 目录 3/ 目录 4 目录 5 目录 6/目录7创建表格
创建表`文件系统`(`id` 整数,`目录名`文本,主键(`id`));创建表`tree_path`(`祖先`整数,`后代`整数,主键(`祖先`,`后代`));将目录插入filesystem表
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (1, 'ROOT');插入文件系统 (id, dirname) VALUES (2, 'Dir2');插入文件系统 (id, dirname) VALUES (3, 'Dir3');插入文件系统 (id, dirname) VALUES (4, 'Dir4');插入文件系统 (id, dirname) VALUES (5, 'Dir5');插入文件系统 (id, dirname) VALUES (6, 'Dir6');插入文件系统 (id, dirname) VALUES (7, 'Dir7');创建闭包表路径
INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先,后代) VALUES (1, 1);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (1, 2);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (1, 3);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (1, 4);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (1, 5);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (1, 6);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (1, 7);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (2, 2);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (2, 4);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (2, 5);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (2, 7);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (3, 3);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (3, 6);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (4, 4);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (4, 7);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (5, 5);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (6, 6);INSERT INTO tree_path (祖先, 后代) VALUES (7, 7);运行一些查询
# (ROOT) 和子目录SELECT f.id, f.dirname FROM 文件系统 fJOIN tree_path tON t.descendant = f.id哪里 t.ancestor = 1;+----+---------+|身份证 |目录名 |+----+---------+|1 |根||2 |目录2 ||3 |目录3 ||4 |目录4 ||5 |目录5 ||6 |目录6 ||7 |目录7 |+----+---------+#目录3和子目录选择 f.id, f.dirnameFROM 文件系统 fJOIN tree_path tON t.descendant = f.id哪里 t.ancestor = 3;+----+---------+|身份证 |目录名 |+----+---------+|3 |目录3 ||6 |目录6 |+----+---------+# Dir5 和父目录选择 f.id, f.dirnameFROM 文件系统 fJOIN tree_path tON t.ancestor = f.idWHERE t.descendant = 5;+----+---------+|身份证 |目录名 |+----+---------+|1 |根||2 |目录2 ||5 |目录5 |+----+---------+# Dir7 和父目录选择 f.id, f.dirnameFROM 文件系统 fJOIN tree_path tON t.ancestor = f.idWHERE t.descendant = 7;+----+---------+|身份证 |目录名 |+----+---------+|1 |根||2 |目录2 ||4 |目录4 ||7 |目录7 |+----+---------+选择 f.id, f.dirnameFROM 文件系统 fJOIN tree_path tON t.ancestor = f.idWHERE t.descendant = (选择 ID从文件系统WHERE dirname LIKE '%7%');+----+---------+|身份证 |目录名 |+----+---------+|1 |根||2 |目录2 ||4 |目录4 ||7 |目录7 |+----+---------+I want to store the directories (present on the disk) into a database, maintaining their hierarchical/tree structure.
Here's a figure:
(ROOT)
/
Dir2 Dir3
/
Dir4 Dir5 Dir6
/
Dir7
I am using the SQLite database.
Please suggest me:
the SQL query to store above structure in SQLite database, and
a query to retrieve full path of the directory when I select one.
i.e. suppose I select
Dir7then I should get the full path likeROOT/Dir2/Dir4/Dir7
Here's a quick closure table example for SQLite. I've not included the statements for inserting items into an existing tree. Instead, I've just created the statements manually. You can find the insert and delete statements in the Models for hierarchical data slides.
For the sake of my sanity when inserting the IDs for the directories, I renamed the directories to match their IDs:
(ROOT)
/
Dir2 Dir3
/
Dir4 Dir5 Dir6
/
Dir7
Create tables
CREATE TABLE `filesystem` (
`id` INTEGER,
`dirname` TEXT,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
);
CREATE TABLE `tree_path` (
`ancestor` INTEGER,
`descendant` INTEGER,
PRIMARY KEY (`ancestor`, `descendant`)
);
Insert directories into filesystem table
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (1, 'ROOT');
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (2, 'Dir2');
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (3, 'Dir3');
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (4, 'Dir4');
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (5, 'Dir5');
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (6, 'Dir6');
INSERT INTO filesystem (id, dirname) VALUES (7, 'Dir7');
Create the closure table paths
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 1);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 2);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 3);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 4);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 5);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 6);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (1, 7);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (2, 2);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (2, 4);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (2, 5);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (2, 7);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (3, 3);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (3, 6);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (4, 4);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (4, 7);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (5, 5);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (6, 6);
INSERT INTO tree_path (ancestor, descendant) VALUES (7, 7);
Run some queries
# (ROOT) and subdirectories
SELECT f.id, f.dirname FROM filesystem f
JOIN tree_path t
ON t.descendant = f.id
WHERE t.ancestor = 1;
+----+---------+
| id | dirname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | ROOT |
| 2 | Dir2 |
| 3 | Dir3 |
| 4 | Dir4 |
| 5 | Dir5 |
| 6 | Dir6 |
| 7 | Dir7 |
+----+---------+
# Dir3 and subdirectories
SELECT f.id, f.dirname
FROM filesystem f
JOIN tree_path t
ON t.descendant = f.id
WHERE t.ancestor = 3;
+----+---------+
| id | dirname |
+----+---------+
| 3 | Dir3 |
| 6 | Dir6 |
+----+---------+
# Dir5 and parent directories
SELECT f.id, f.dirname
FROM filesystem f
JOIN tree_path t
ON t.ancestor = f.id
WHERE t.descendant = 5;
+----+---------+
| id | dirname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | ROOT |
| 2 | Dir2 |
| 5 | Dir5 |
+----+---------+
# Dir7 and parent directories
SELECT f.id, f.dirname
FROM filesystem f
JOIN tree_path t
ON t.ancestor = f.id
WHERE t.descendant = 7;
+----+---------+
| id | dirname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | ROOT |
| 2 | Dir2 |
| 4 | Dir4 |
| 7 | Dir7 |
+----+---------+
SELECT f.id, f.dirname
FROM filesystem f
JOIN tree_path t
ON t.ancestor = f.id
WHERE t.descendant = (
SELECT id
FROM filesystem
WHERE dirname LIKE '%7%'
);
+----+---------+
| id | dirname |
+----+---------+
| 1 | ROOT |
| 2 | Dir2 |
| 4 | Dir4 |
| 7 | Dir7 |
+----+---------+
这篇关于文件系统中目录路径的分层/树数据库的文章就介绍到这了,希望我们推荐的答案对大家有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持编程学习网!
本文标题为:文件系统中目录路径的分层/树数据库


- 更改自动增量起始编号? 2021-01-01
- 使用 Oracle PL/SQL developer 生成测试数据 2021-01-01
- 如何将 SonarQube 6.7 从 MySQL 迁移到 postgresql 2022-01-01
- 在SQL中,如何为每个组选择前2行 2021-01-01
- 导入具有可变标题的 Excel 文件 2021-01-01
- 如何将 Byte[] 插入 SQL Server VARBINARY 列 2021-01-01
- 以一个值为轴心,但将一行上的数据按另一行分组? 2022-01-01
- 如何使用 pip 安装 Python MySQLdb 模块? 2021-01-01
- SQL 临时表问题 2022-01-01
- 远程 mySQL 连接抛出“无法使用旧的不安全身份验证连接到 MySQL 4.1+"来自 XAMPP 的错误 2022-01-01